Siglec Programs
Leveraging Siglec antibodies to outsmart cancer
What are Siglecs?
We are developing a Siglec agonist fusion protein and an antagonist anti-Siglec antibody to reduce immune-related adverse events (irAEs) and fight solid tumors.
The binding of Siglecs to sialic acids plays a crucial role in cell-cell interaction and communication, particularly in the immune system.1 We are developing Siglec agonist fusion protein and an antagonist anti-Siglec antibody to respectfully reduce irAE and fight solid tumors.
1. CD24 and Siglec-10 selectively repress tissue damage-induced immune responses. Chen GY, Tang J, Zheng P, Liu Y. Science. 2009 Mar 27;323(5922):1722-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1168988.
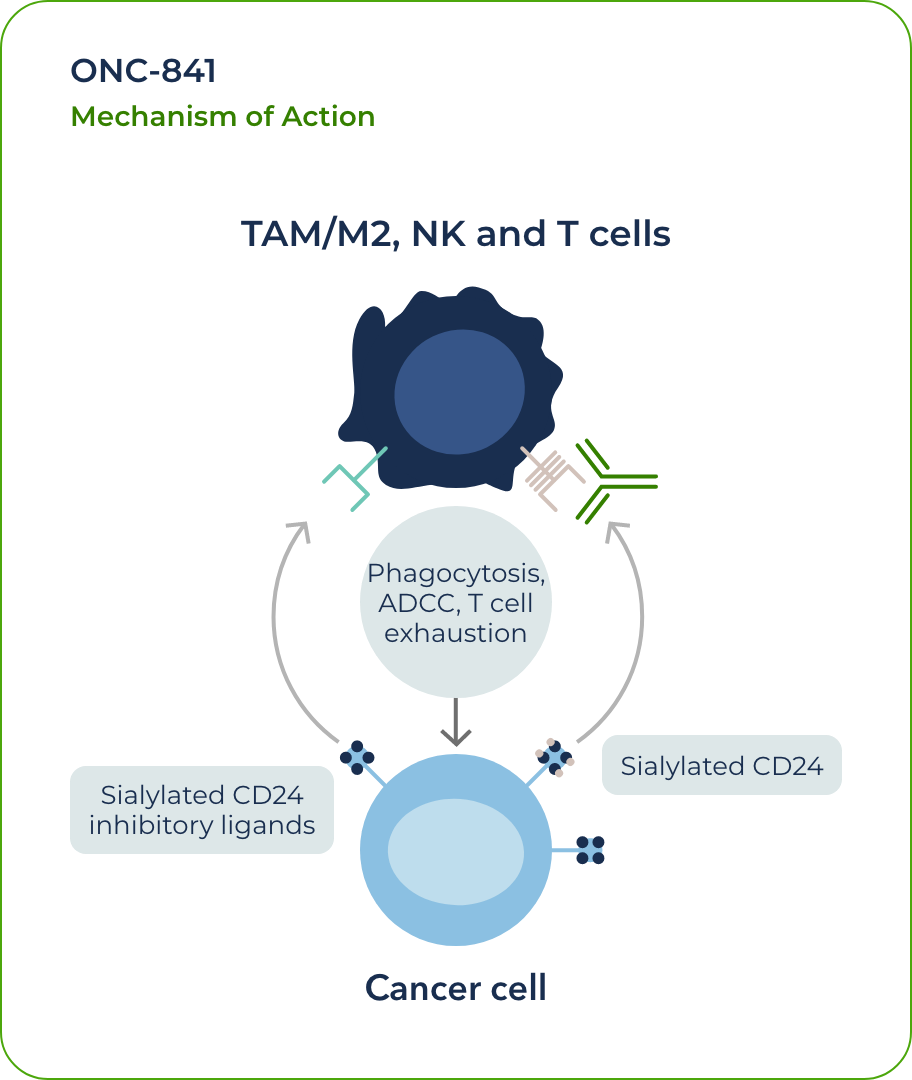
ONC-841: an anti-Siglec mAb for solid tumors
Siglec-10 is a protein that can potentially suppress the immune system’s ability to fight off diseases.
Some cancers exploit Siglec-10 signaling to avoid being recognized and attacked by the immune system. Targeting this protein in solid tumors may enable the patient’s immune system to better fight cancer.2 Our potential first-in-class anti-Siglec10 mAb has shown antitumor activity in syngeneic xenograft models.
See how we turn our science into action.
2. Barkal AA, Brewer RE, Markovic M, Kowarsky M, Barkal SA, Zaro BW, Krishnan V, Hatakeyama J, Dorigo O, Barkal LJ, Weissman IL. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7769):392-396. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1456-0.
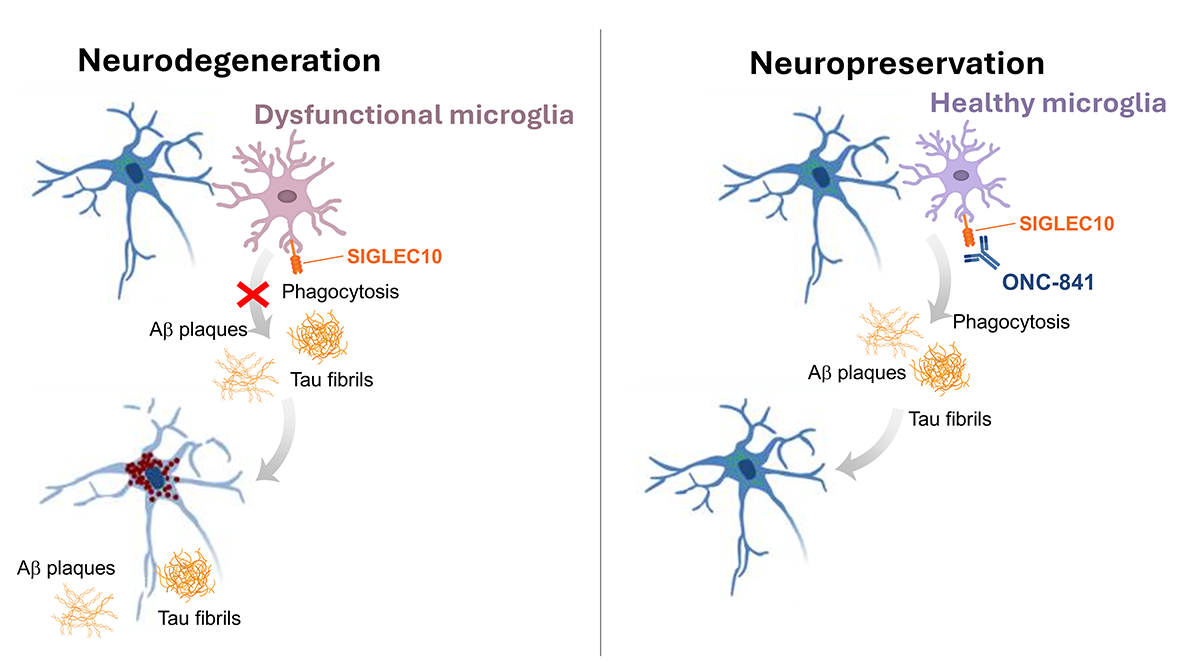
ONC-841 and neuro-degeneration
Normalizing microglia function for clearance of protein aggregates
- ONC-841 effectively targets SIGLEC10 on microglia in brain
- Preclinical studies reveal its in vivo activity in ameliorating Ab and pTau pathology in mice
- Preclinical studies provide rationale for testing the drug in Alzeimer’s and possibly other neuro-degenerative diseases
- Clinical study on early-stage Alzheimer’s disease will be launched in US in 1H 2025